Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) is a powerful new feature of the 2nd Gen AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ CPUs.1 Much like traditional overclocking, PBO is designed to improve multithreaded performance. But unlike traditional overclocking, Precision Boost Overdrive preserves all the automated intelligence built into a smart CPU like Ryzen: Precision Boost 2 remains enabled for on-demand performance, XFR 2 still enables higher performance with better cooling, and the CPU still lowers clocks and voltages to save power at idle. As you can see, Precision Boost Overdrive is sort of a “best of all worlds” approach to overclocking that manual mode usually doesn’t offer. But how does PBO work? Let’s find out in three easy steps.
Step 1: What Controls Boost
All 2nd Gen AMD Ryzen-branded Processors use Precision Boost 2, which intelligently leverages a large network of sensors built into the CPU to determine whether it’s okay to boost. These sensors measure and react in a very fast loop: up to 1000 times per second. Though there are many data points being measured, the most important are:
- SoC Power (“PPT Limit”): measured in watts, the amount of power the CPU can draw before boost levels off
- VRM Current (“TDC Limit”): measured in amps, the amount of current we let the motherboard deliver to the CPU before boost levels off
- Temp (°C): measured in degrees Celsius, the temperature the CPU can reach before boost levels off
If the sensors detect that the CPU isn’t close to one of these limits, Precision Boost 2 sees opportunity to raise clockspeeds on as many cores as it can.
It is useful to imagine these three thresholds (“platform limits”) as a triangle, shown below, where the labeled corners are something like the RPM redline on your car. Inside of that, a safer and more reliable triangle that represents the factory configuration of your CPU.
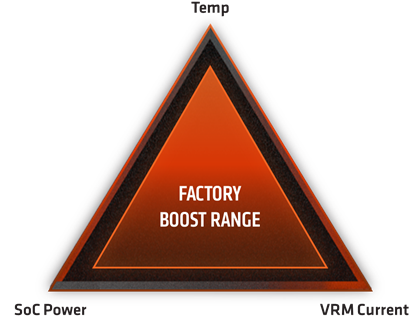 Figure 1: Precision Boost 2 leverages extra thermal and electrical capacity to enable higher performance. The CPU’s factory configuration is aggressive, without pushing the CPU to the red line in power or temperatures.
Figure 1: Precision Boost 2 leverages extra thermal and electrical capacity to enable higher performance. The CPU’s factory configuration is aggressive, without pushing the CPU to the red line in power or temperatures.
Step 2: More Room to Play
If the size of the imaginary triangle largely determines whether or not the CPU can boost, what if the triangle were simply larger? In the previous diagram, you may have noticed that there’s some empty space between the factory CPU configuration and the platform limits. That empty space is what users are filling up when they overclock their CPU, and it’s the same space the 2nd Gen AMD Ryzen Threadripper CPU consumes when PBO is enabled. Let’s see how that new triangle might look!
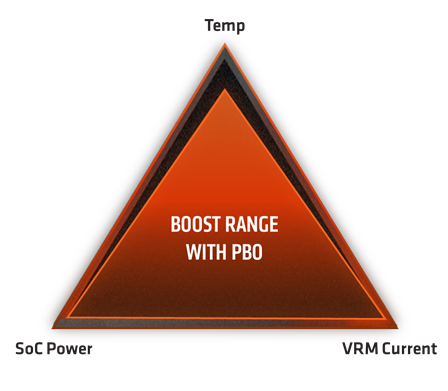 Figure 2: Precision Boost Overdrive gives Precision Boost 2 more "room to play" before pulling back on boost. More cores, more frequency, more often!
Figure 2: Precision Boost Overdrive gives Precision Boost 2 more "room to play" before pulling back on boost. More cores, more frequency, more often!
As you can see, the PPT and TDC Limits have been embiggened to let the platform draw more power. That extra power is directly converted into higher average clockspeeds on more cores for a longer period of time. PBO even communicates with your motherboard to understand how much extra VRM current capacity (TDC) it can provide!
Step 3: The Benefits of Precision Boost Overdrive
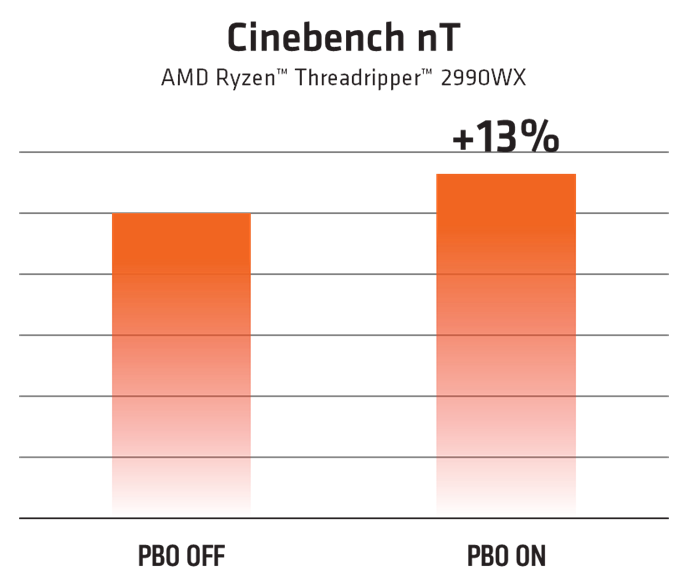
By now we know that Precision Boost Overdrive unleashes a more aggressive version of Precision Boost 2 that preserves the smart frequency and voltage management that users like. The performance upside for PBO can be significant: up to 13% more multithread performance!2 That’s not dissimilar to what a user might gain with manual overclocking, but PBO can accomplish it at the touch of a button in the latest version of AMD Ryzen™ Master.
Precision Boost Overdrive: A Smarter Way to Overclock
Taking your feedback seriously is a critical objective for us, as is using the Ryzen CPU's intelligence in new and beneficial ways. We knew we could bring those two goals together with Precision Boost Overdrive! The result is awesome: a new type of overclocking that combines smart boost control, idle power savings, factory max boost clock, and higher nT performance. We hope you enjoy!
Robert Hallock is a technical marketing guy for AMD's CPU division. His postings are his own opinions and may not represent AMD’s positions, strategies or opinions. Links to third party sites are provided for convenience and unless explicitly stated, AMD is not responsible for the contents of such linked sites and no endorsement is implied.
Footnotes:
1. Precision Boost Overdrive requires a 2nd Gen AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper processor with AMD X399 chipset motherboard. Because Precision Boost Overdrive enables operation of the processor outside of specifications and in excess of factory settings, use of the feature invalidates the AMD product warranty and may also void warranties offered by the system manufacturer or retailer. GD-128
2. Testing conducted by AMD Performance Labs as of 7/16/2018. “Multithread performance” defined as Cinebench R15 nT. Results presented in order of Precision Boost Overdrive OFF vs. ON: 5096 vs. 5795 (%13 faster). AMD System configuration: AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ 2990WX, Enermax 360 CLC @ 20°C ambient temperature, 4x8GB DDR4-3200 (14-14-14-28-1T), Asus Zenith X399 Extreme (BIOS 0008), GeForce GTX 1080 Ti (driver 398.36), Windows® 10 x64 1803, Samsung 850 Pro SSD, Western Digital Black 2TB HDD. Results may vary with system configuration. Precision Boost Overdrive requires a 2nd Gen AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper processor with AMD X399 chipset motherboard. Because Precision Boost Overdrive enables operation of the processor outside of specifications and in excess of factory settings, use of the feature invalidates the AMD product warranty and may also void warranties offered by the system manufacturer or retailer.