- AMD Community
- Blogs
- Server Processors
- 3rd Gen AMD EPYC™ Processors Extend Big Data Perfo...
3rd Gen AMD EPYC™ Processors Extend Big Data Performance Leadership
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Businesses generate high volumes of interconnected structured, semi structured, and unstructured data every day. Big Data Analytics is the often-complex process of examining this data to uncover information—such as hidden patterns, correlations, market trends and customer preferences—that can help organizations make informed business decisions.
AMD has been working with our partner ecosystem to create optimal infrastructure solutions for Big Data Analytics. This includes the popular Apache® Hadoop® framework that facilitates distributed processing of large data sets. We have several customers who have implemented Big Data Analytics deployments on AMD EPYC™ based servers because of their ongoing performance, scalability, and total cost of ownership advantages demonstrated through industry standard benchmarks.[1]
TPC Express Benchmark™ HS (TPCx-HS) is a popular industry standard for benchmarking Hadoop-based Big Data Analytics systems that enables performance and price-performance comparisons in a technically rigorous, directly comparable, and vendor-neutral manner. TPCx-HS stresses both the hardware and software stacks, including the execution engine and Hadoop Filesystem API compatible layers. TPCx-HS can assess a broad range of system topologies and implementation methodologies and produce results that are highly relevant to Big Data and analytics hardware and software systems.
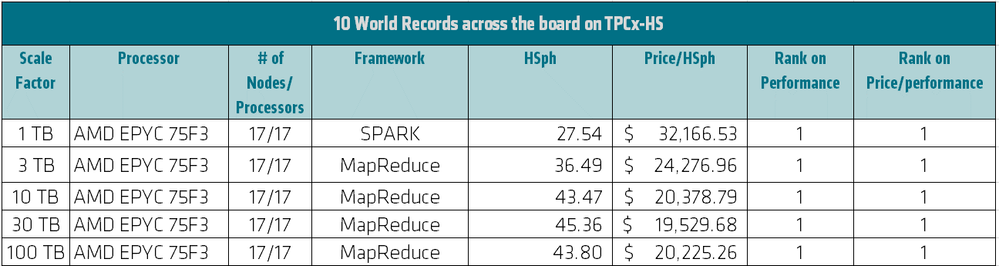
Today, AMD EPYC 7003 Series Processors dominate the performance world records at every scale factor, as shown in Figure 1 and at the AMD EPYC™ Processor World Records page. The results in Figure 1 were obtained using a Supermicro cluster.[2]
Figure 1: Performance and price/performance rankings of 3rd Gen AMD EPYC processors[2]
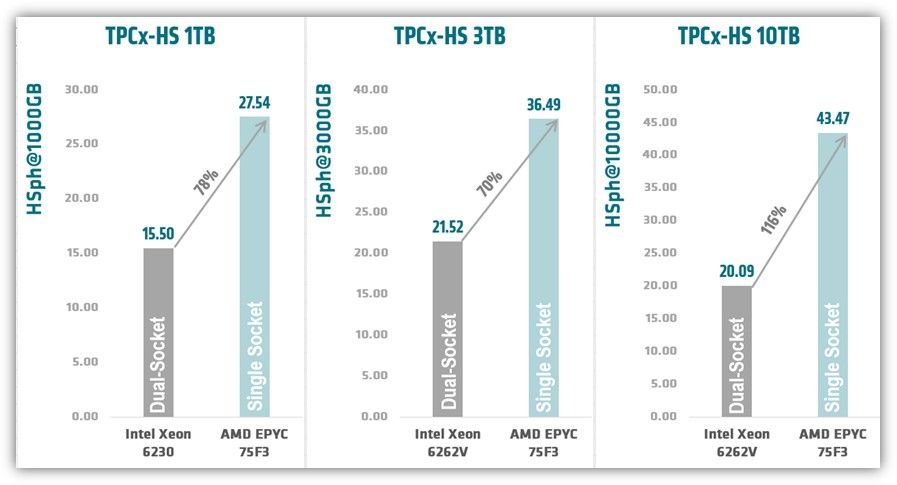
I also want to show how these results stack up against the competition. Figure 2 shows that AMD EPYC-based systems show 78%, 70%, and 116% better price-performance at 1TB, 3TB, and 100TB, respectively.[3,4,5] It is important to note that each AMD EPYC-based server included only one processor while the other servers each contained two processors. This demonstrates the viability of single socket servers to offer you the most optimal solutions.
Figure 2: 1x AMD EPYC 75F3 TPCx-HS performance vs. 2x Intel® Xeon® 6262V on CDP Private Cloud
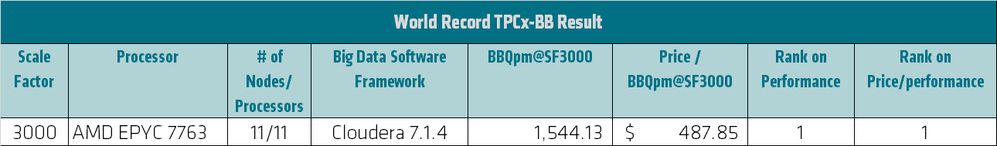
TPC Express Benchmark BB (TPCx-BB) is another popular benchmark for Hadoop-based Big Data systems. This benchmark measures the performance of both hardware and software components by executing 30 frequently-performed analytical queries in the context of retailers with both physical and online presence. Queries are expressed in SQL for structured data and in machine learning algorithms for semi-structured and unstructured data. The SQL queries can use Hive or Spark, while the machine learning algorithms use machine learning libraries, user defined functions, and procedural programs. A single-socket AMD EPYC-based system delivered the top result in 3000GB scale factor, as shown in Figure 3.[6] A cluster of Dell EMC PowerEdge 7515 servers powered by AMD EPYC 7763 processors delivered 1,533.13 BBQpm at $487.5/BBQpm.
Figure 3: Single-socket AMD EPYC 7763 performance on TPCx-BB benchmark
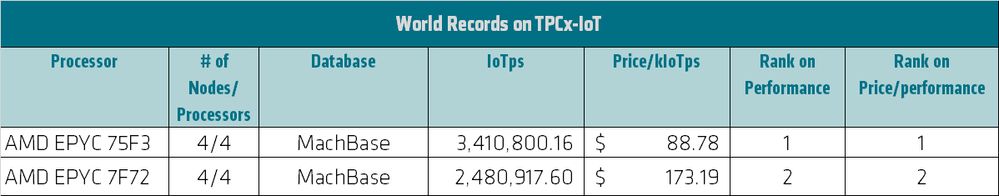
I also want to mention the TPC Express Benchmark IoT (TPCx-IOT) for IoT Gateway systems. This benchmark is very relevant in today's connected world as more and more smart devices connect to the internet. TPCx-IoT is the industry’s first benchmark that allows direct comparison of different software and hardware solutions for IoT gateways. Gateway systems reside between edge architecture and the back-end datacenter where they perform functions such as data aggregation, real-time analytics, and persistent storage. TPCx-IoT was specifically designed to provide verifiable performance, price-performance, and availability metrics for commercially available systems that typically ingest massive amounts of data from large numbers of devices while running real-time analytic queries. The workload represents typical IoT gateway activities running on commercially available hardware and software platforms. I am very excited to say that AMD EPYC-powered systems deliver top performance and price-performance, as you can see in Figure 4.[7]
Figure 4: AMD EPYC-powered system deliver top performance and price performance on IoT workloads
These results demonstrate that AMD EPYC based servers are the ideal choice for your big data analytics deployments.[2] Some of our key Big Data Analytics partnerships include:
I would like to thank our ecosystem partners for their continued support.
Raghu Nambiar is Corporate Vice President of Data Center Ecosystems and Solutions for AMD. His postings are his own opinions and may not represent AMD’s positions, strategies or opinions. Links to third party sites are provided for convenience and unless explicitly stated, AMD is not responsible for the contents of such linked sites and no endorsement is implied.
Footnotes
AMD EPYC processor-based platforms held world record performance prior to new results: AMD EPYC 75F3 HSph@1TB 24.69 : http://tpc.org/5551 HSph@3TB 34.52: http://tpc.org/5548 HSph@100TB 43.76: http://tpc.org/5552; AMD EPYC 7502P : HSph@10TB 23.66: http://tpc.org/5532 ; HSph@30TB 25.47 http://tpc.org/5533 ; see also: https://www.amd.com/en/processors/epyc-world-records
AMD EPYC 75F3 17 Nodes, 17 processors, 544 cores 27.54 HSph@1TB, 32,166.53 USD per HSph@1TB, 2 world records in price and price-performance for 1TB SF http://tpc.org/5553 ; 3rd Gen AMD EPYC 75F3 17 Nodes, 17 processors, 544 cores 36.49 HSph@3TB, 24,276.96 USD per HSph@3TB, 2 world records in price and price-performance for 3TB SF http://tpc.org/5554; AMD EPYC 75F3 17 Nodes, 17 processors, 544 cores 43.47 HSph@10TB, 20,378.79 USD per HSph@10TB, 2 world records in price and price-performance for 1-TB SF http://tpc.org/5555; AMD EPYC 75F3 17 Nodes, 17 processors, 544 cores 45.36 HSph@30TB, 19,529.68 USD per HSph@30TB, 2 world records in price and price-performance for 30TB SF http://tpc.org/5556 ; AMD EPYC 75F3 17 Nodes, 17 processors, 544 cores 43.80 HSph@100TB, 20,225.26 USD per HSph@100TB, 2 world records in price and price-performance for 100TB SF http://tpc.org/5557
AMD EPYC 75F3 17 Nodes, 17 processors, 544 cores 27.54 HSph@1TB, 32,166.53 USD per HSph@1TB, http://tpc.org/5553 . Intel Xeon 6230 17 Nodes, 34 processors, 680 cores 15.60 HSph@1TB, 65,021.16 USD per HSph@1TB, http://tpc.org/5541 . 27.54/15.50 = 78%
AMD EPYC 75F3 17 Nodes, 17 processors, 544 cores 36.49 HSph@3TB, 24,276.96 USD per HSph@3TB, http://tpc.org/5554 . Intel Xeon 6262V 17 Nodes,34 processors, 808 cores 21.52 HSph@3TB, 91,276.91 USD per HSph@3TB, http://tpc.org/5544 . 36.49/21.52=70%
AMD EPYC 75F3 17 Nodes, 17 processors, 544 cores 43.47 HSph@10TB, 20,378.79 USD per HSph@10TB, http://tpc.org/5555 . Intel Xeon 6262V 17 Nodes, 34 processors, 808 cores 20.09 HSph@10TB, 97,773.97 USD per HSph@10TB, http://tpc.org/5545 . 43.47/20.09=116%
- AMD EPYC 7763 11 Nodes, 11 processors, 704 cores 1,544.13 BBQpm@SF3000 487.85 USD per BBQpm@SF3000 http://tpc.org/3518
- AMD EPYC 75F3 4 Nodes, 4 processors, 160 cores 3,410,800.16 IoTps 88.78 USD per kIoTps http://tpc.org/5766 ; AMD EPYC 7F72 4 Nodes, 4 processors, 136 cores 2,480,917.60 IoTps 173.19 USD per kIoTps http://tpc.org/5765
-
AI & Machine Learning
25 -
AMD
1 -
AMD Instinct Accelerators Blog
1 -
Cloud Computing
35 -
Database & Analytics
26 -
EPYC
115 -
EPYC Embedded
1 -
Financial Services
18 -
HCI & Virtualization
29 -
High-Performance Computing
36 -
Instinct
9 -
Supercomputing & Research
9 -
Telco & Networking
14 -
Zen Software Studio
4
- « Previous
- Next »