- AMD Community
- Blogs
- EPYC Processors
- 4th Gen AMD EPYC™ CPUs Empower Leadership SAP® Sal...
4th Gen AMD EPYC™ CPUs Empower Leadership SAP® Sales & Distribution (SAP SD) 2-Tier Performance
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
4th Gen AMD EPYC™ processors continue to redefine data center performance, power efficiency, and total cost of ownership through relentless innovation. This dual focus on performance and efficiency underscores the AMD commitment to empowering businesses with cutting-edge solutions for their data center needs. Presently, the robust AMD EPYC ecosystem comprises over 250 distinct server designs and more than 800 unique cloud instances. AMD EPYC processors hold over 300 world records for performance across various benchmarks, encompassing Business applications, Technical Computing[1], Data Management, Data Analytics, Digital Services, Media and Entertainment, and Infrastructure Solutions.
SAP Sales and Distribution (SAP SD) is a pivotal logistics module within SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software. This module plays a crucial role in storing and overseeing critical business data across four primary components:
- Organization Structure: SAP SD manages the organizational setup within the software by defining various units, divisions, and departments involved in the sales and distribution processes.
- Master Data: SAP SD maintains essential master data that includes both customer information (such as customer profiles, contact details, and transaction history) and material data (such as product specifications, inventory levels, and pricing details).
- Business Processes: SAP SD orchestrates end-to-end sales cycles, encompassing activities like order processing, pricing, delivery, billing, and payment handling. It ensures seamless coordination and execution of sales-related operations.
- Reporting: SAP SD facilitates comprehensive reporting capabilities that enable users to generate insightful analyses and reports based on sales and distribution data. These reports provide valuable insights into sales performance, customer trends, inventory management, and revenue generation.
Overall, SAP SD plays a vital role in streamlining sales and distribution operations, enhancing efficiency, and enabling informed decision-making within organizations leveraging SAP ERP software.
The SAP-SD 2-Tier benchmark evaluates hardware performance by measuring database performance in SAP Application Performance Standard units (SAPS). SAPS is a hardware-independent unit that quantifies system performance within the SAP environment. SAPS are derived from the Sales and Distribution (SD) benchmark and reflect the system's capacity to handle SAP workloads. During SAP benchmark testing, vendors use their standard methodology to determine the system's capacity to support SD users. Each module within the benchmark carries a weightage that converts users into a Normalized SD (NSD) number. SAPS is calculated from the NSD. SAPS results from the SAP SD benchmark help SAP customers size their SAP systems and plan their infrastructure footprint. This benchmark enables customers to conduct Proof-of-Concepts (POCs), anticipate future growth, and compare platforms to select the optimal hardware configuration for their SAP solution.
On Bare Metal
The compute-intensive nature of the SAP SD workload make 4th Gen AMD EPYC processors (9004 series) an optimal choice for deploying SAP applications on bare metal servers. These processors maximize performance by harnessing significant improvements in Instructions per Cycle (IPC), faster memory access, increased L3 cache sizes, and higher core density compared to prior-generation AMD EPYC processors.
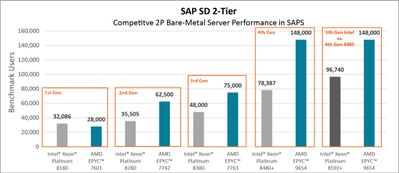
Figure 1 demonstrates the performance improvements attained with "top of stack" processor SKUs throughout the four generations of general-purpose AMD EPYC processors. Additionally, it highlights the consistent outperformance of 2nd Gen AMD EPYC processors and newer generations compared to corresponding generations of Intel® Xeon® processors. Notably, 4th Gen AMD EPYC processors exceed the performance of 5th Gen Intel® Xeon® processors by 53%.[2]
Figure 1: Generational and competitive SAP SD 2-Tier performance uplifts on 2P bare-metal systems (click image for larger view)
In the Cloud
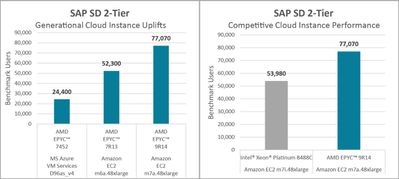
Looking to deploy SAP in the cloud? AMD EPYC processors offer comprehensive support here as well. The left side of Figure 2 illustrates significant performance enhancements across 2nd, 3rd, and 4th Gen AMD EPYC processors on Microsoft Azure and Amazon EC2 cloud instances. The right side of Figure 2 shows how an Amazon EC2 m7a.48xlarge instance powered by 4th Gen AMD EPYC processors outperforms a comparable Amazon EC2 m7i.48xlarge instance powered by Intel Xeon Platinum 8488C processors.[3]
Figure 2: Generational SAP SD 2-Tier performance on cloud instances (click image for larger view)
Comparing SAP-SD Performance with SPEC CPU® 2017 (Curiosity Analysis)
Many individuals strive to relate how the SPEC CPU® 2017 benchmark is truly representative of real world enterprise applications. The SPEC CPU® 2017 benchmark holds significant industry prominence because its performance measurements thoroughly stress a system's processor, memory subsystem, and compiler. These measurements enable users to compare the performance of various systems effectively. SPEC CPU 2017 comprises four suites: SPECspeed® 2017 Integer, SPECspeed® 2017 Floating Point, SPECrate® 2017 Integer, and SPECrate® 2017 Floating Point. SPECspeed metrics assess the time taken to complete a workload, while SPECrate metrics gauge the amount of work accomplished per unit of time.
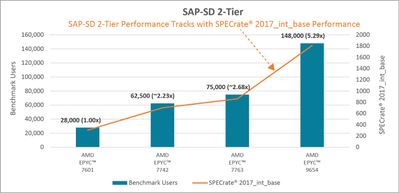
Among these metrics, SPECrate 2017 Integer demonstrates a strong correlation with the SAP-SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users metric, as depicted in Figure 3. This correlation is particularly valuable for SAP SD 2-Tier sizing because it allows deriving reliable SAP-SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users estimates based on the SPECrate 2017 Integer metric results published for every EPYC SKU.[4]
Figure 3: SPECrate® 2017_int-base performance tracks with SAP SD 2-Tier performance (click image for larger view)
Conclusion
The SAP SD benchmark results underscore the excellent performance of AMD EPYC processors both on bare metal and in the cloud. 4th Gen AMD EPYC processors support cutting-edge technologies, including "Zen 4" cores built on 5nm process technology, up to 12 channels of DDR5 memory with supported memory speeds up to 4800GHz, and up to 128 (1P) or 160 (2P) lanes of PCIe® Gen5 delivering double the transfer rate of PCIe Gen4. The 3rd Gen Infinity Fabric™ doubles the data transfer rate of the 2nd Gen Infinity Fabric, while AMD Infinity Guard technology enhances data security during use.[5] Additionally, AMD EPYC 97x4 processors and AMD EPYC 9004 processors with AMD 3D V-Cache™ technology expands the lineup of 4th Gen AMD EPYC processors, with optimized models for cloud infrastructure and memory-bound workloads, respectively.
Platforms powered by AMD EPYC processors are supported by all major operating systems, hypervisors, and leading cloud service providers. Most application binaries designed for standard x86 platforms seamlessly run on AMD EPYC platforms, but users can further improve the performance and experience for specific workloads by tuning the hardware, BIOS, operating system, and/or application framework. AMD actively collaborates with its ecosystem of independent software vendors (ISVs) to drive software changes that leverage the unique AMD EPYC architecture to unlock higher levels of differentiated performance compared to other x86 platforms. AMD also offers guidance on the best CPU tuning practices to achieve optimal performance with Gen AMD EPYC processors via the AMD Documentation Hub, which hosts a large library of AMD EPYC Tuning Guides.
AMD offers a range of cutting-edge technologies beyond AMD EPYC processors:
- AMD Instinct™ accelerators are designed to drive discoveries at exascale, enabling scientists to tackle some of the most pressing challenges in fields like scientific research, artificial intelligence, and high-performance computing.
- AMD Pensando™ solutions provide highly programmable, software-defined cloud, compute, networking, storage, and security features wherever data is located. They aim to enhance productivity, performance, and scalability compared to current architectures.
- AMD FPGA and Adaptive SoC technologies encompass highly flexible and adaptive Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), hardware adaptive System-on-Chips (SoCs), and the Adaptive Compute Acceleration Platform (ACAP) processing platforms. These solutions enable rapid innovation across various technologies, spanning from endpoint devices to edge computing to the cloud.
Raghu Nambiar is a Corporate Vice President of Data Center Ecosystems and Solutions for AMD. His postings are his own opinions and may not represent AMD’s positions, strategies, or opinions. Links to third party sites are provided for convenience and unless explicitly stated, AMD is not responsible for the contents of such linked sites and no endorsement is implied.
References
- GD-204: “Technical Computing” or “Technical Computing Workloads” as defined by AMD can include: electronic design automation, computational fluid dynamics, finite element analysis, seismic tomography, weather forecasting, quantum mechanics, climate research, molecular modeling, or similar workloads.
- For Figure 1:
- Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8180 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 32,086: https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2018/Cert18060.pdf
- AMD EPYC™ 7601 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 28,000: https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2018/Cert18014.pdf
- Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8280 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 35,505: https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2019/Cert19026.pdf
- AMD EPYC™ 7742 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 62,500: https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2019/Cert19047.pdf
- Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8380 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 48,000: https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2023/Cert23019.pdf
- AMD EPYC™ 7763 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 75,000: https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2021/Cert21021.pdf
- Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8480+ SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 78,387: https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2023/Cert23027.pdf
- Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8592+ SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 96,740: https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2023/Cert23077.pdf
- AMD EPYC™ 9654 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 148,000: https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2022/Cert22029.pdf
- For Figure2:
- Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine Services D96as_v4 AMD EPYC™ 7452 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 24,400
https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2020/Cert20017.pdf - Amazon EC2 m6a.48xlarge AMD EPYC™ 9R13 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 52,300
https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2022/Cert22002.pdf - Amazon EC2 m7a.48xlarge AMD EPYC™ 9R14 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 77,070
https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2023/Cert23055.pdf - Amazon EC2 m7i.48xlarge Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8488C SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 53,980
https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2023/Cert23061.pdf - For Figure 3:
- SPEC®, SPEC CPU®, SPECrate®, and SPECspeed® are registered trademarks of Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. Learn more at spec.org. SAP and SAP logo are the trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE (or an SAP affiliate company) in Germany and in several other countries.
- AMD EPYC™ 7601 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 28,000
https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2018/Cert18014.pdf - AMD EPYC™ 7742 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 62,500
https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2019/Cert19047.pdf - AMD EPYC™ 7763 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 75,000
https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2021/Cert21021.pdf - AMD EPYC™ 9654 SAP SD 2-Tier Benchmark Users 148,000
https://www.sap.com/dmc/benchmark/2022/Cert22029.pdf - AMD EPYC™ 7601 32c 2P SPECrate®2017_int_base 304 https://www.spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2019q2/cpu2017-20190411-11817.html
- AMD EPYC™ 7742 64c 2P SPECrate®2017_int_base 701 https://www.spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2019q4/cpu2017-20191125-20001.html
- AMD EPYC™ 7763 64c 2P SPECrate®2017_int_base 861 https://www.spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2021q4/cpu2017-20211121-30148.html
- AMD EPYC™ 9654 96c 2P SPECrate®2017_int_base 1810 https://www.spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2024q1/cpu2017-20240129-40896.html
- GD-183: AMD Infinity Guard features vary by EPYC™ Processor generations. Infinity Guard security features must be enabled by server OEMs and/or Cloud Service Providers to operate. Check with your OEM or provider to confirm support of these features. Learn more about Infinity Guard at https://www.amd.com/en/technologies/infinity-guard.